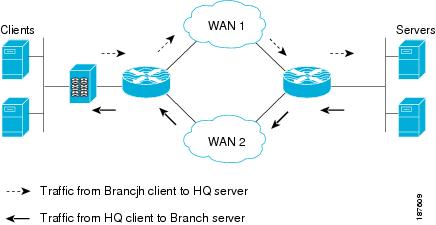
Describe IP operations [ ICMP Unreachable and Redirects ] CCNP
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a supporting protocol in the Internet protocol suite. It is used by network devices, like routers, to send error messages and operational information. ICMP TYPE NUMBERS The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) has many messages that are identified by a "type" field. Type Name Reference ---- ------------------------- --------- 0 Echo Reply [RFC792] 1 Unassigned [JBP] 2 Unassigned [JBP] 3 Destination Unreachable [RFC792] 4 Source Quench [RFC792] 5 Redirect